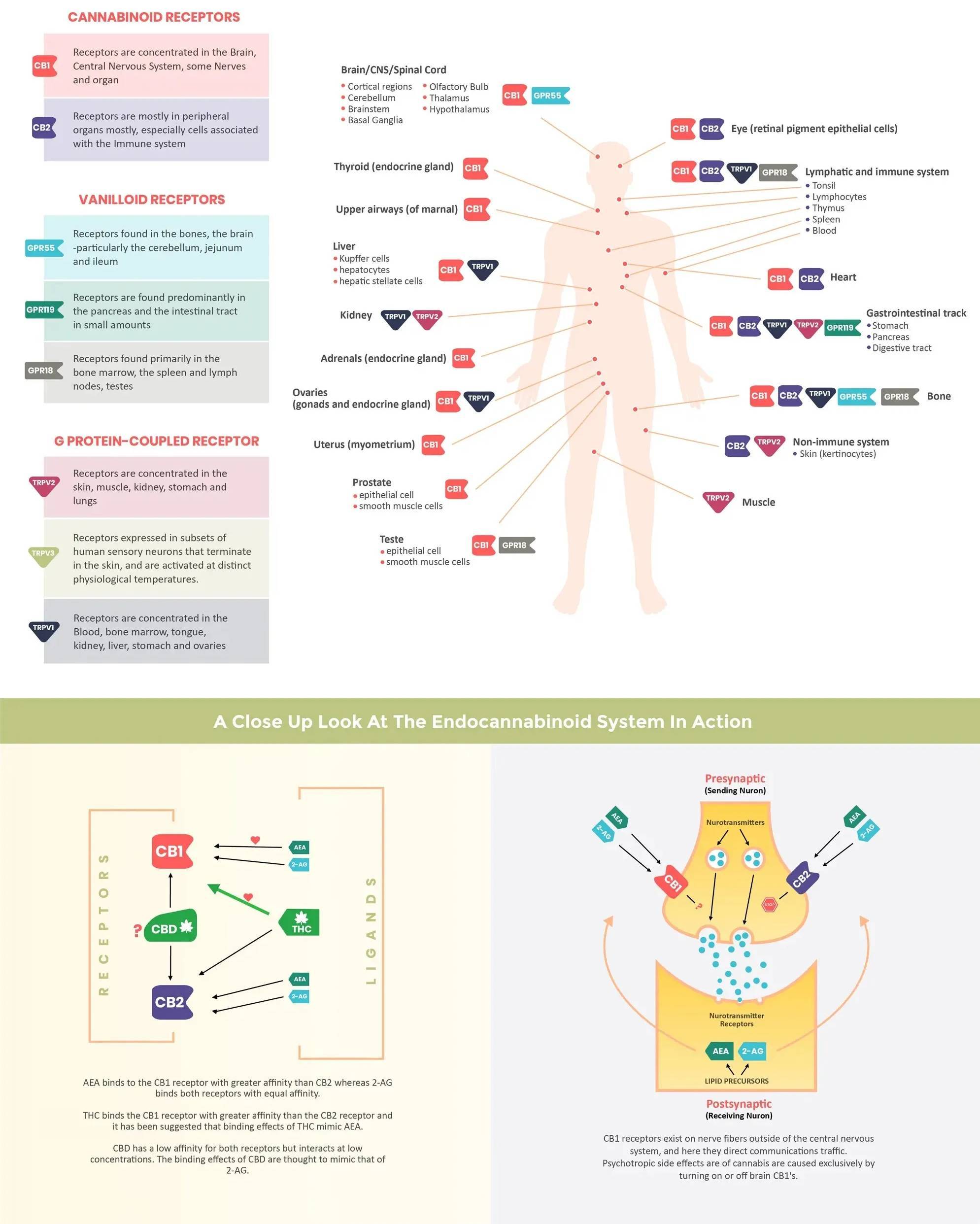
Human Endocannabinoid System (ECS)
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) consists of cannabinoid receptors, endocannabinoids, and their metabolic enzymes.
Receptors fall into 3 groups: Cannabinoid Receptors, Vanilloid Receptors and G Protein Receptors. Cannabinoid Receptors CB1 and CB2 and their endocannabinoid Ligand counterparts,anandamide (AEA) and 2-arachidonoyol-glycerol are found in all mammals and reptiles.
CB1 is densely located in the neocortex, hippocampus, basal ganglia, amygdala, striatum, cerebellum, and hypothalamus. These major brain regions mediate a wide variety of high-order behavioral functions, including learning and memory, executive function decision making, sensory and motor responsiveness, and emotional reactions, as well as feeding and other homeostatic processes.
CB2 receptors are most densly found in immunological tissues and modulate cell fate.
Human endocannabinoids and plant cannabinoids -like THC and CBD- have an affinity for cannabinoid receptors and easily bind to each other, much like a lock and key.
Once activated, cannabinoid receptors inhibit the release of neurotransmitters. The ECS regulates many physiological processes like pain perception, immununity, inflammation as well as neuropathy and metabolism.